FDA-compliant characterisation of nasal spray dynamics and droplet size with laser diffraction
In general, nasal sprays are suitable for local therapy, e.g. as decongestion for blocked nose or treatment of runny nose caused by allergies. Systemic therapy of pharmaceuticals to the nasal mucous membrane is also possible. The nasal delivery is especially of interest if classical ways of absorption are not possible or offer unsatisfactory bioavailability.
During nasal delivery of pharmaceuticals, dosing pump sprays are used as multiple dosage containers. Their triggering provides a defined liquid volume as finely dispersed aerosol. Alternatively, squeeze spray bottles or single dose sprays are used. The penetration depth into the airways and the deposition of atomised liquids are essential for the intended effect. Deposition within the airways is determined by the size of droplets produced; droplets and particles over 20 µm to 30 µm are deposited at the targeted absorption location on the mucous membrane in the first third of the nasal chamber. Residence time and absorption conditions are ideal here. Smaller particles are transported to the lung via breath and settle down there. Particle under 1 µm are likely to be exhaled.
During the approval of new drugs, investigation of droplet size distribution verifies the bioavailability as well as the bioequivalence of generic drugs. Spray applicators should be designed in a way that an optimal droplet size distribution (20 µm to 80 µm) is targeted at a desired dosing volume. This will ensure placement of the active ingredient of desired dosage at the intended place of absorption. The energy needed for atomisation is generated by activating a pump mechanism or by compressing a squeeze bottle. A measurement of droplet size distribution under controlled conditions is recommended during the development of the aerosol as well as during quality control to guarantee the therapeutic effect of a formulation applied as nasal spray.
For a fast determination of the droplet size distribution, HELOS laser diffraction equipped with SPRAYER adapter is used. By triggering a spray shot, spray mist emerges as an extended droplet collective within the measuring zone, and interacts with the laser light. The droplets create a characteristic diffraction pattern which holds all information about the droplet size distribution. Based on the diffraction information, efficient algorithms determine particle or rather droplet size distribution with highest resolution and precision. Relevant triggering parameters of the atomizer, like actuator velocity or force, are adjustable during the measurement and get recorded.
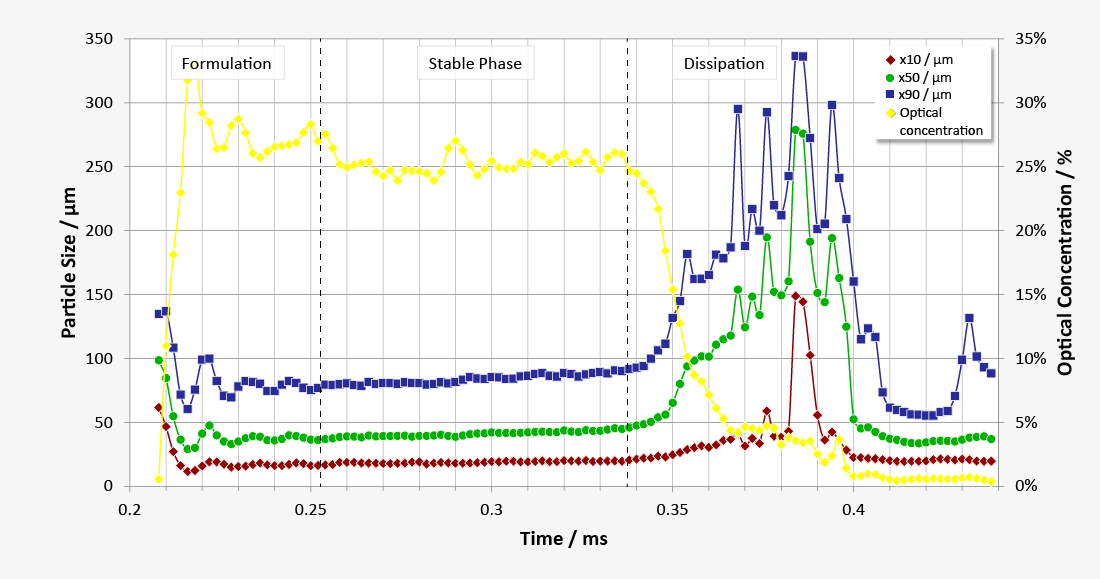
The special feature of a spray measurement is the dynamic change of droplet size during the spray shot. Time-resolved measurement can identify formulation phase, stable phase and dissipation phase, can establish reliable measuring regulations and execute reproducible measurements of the stable phase.
- FDA-compliant characterisation of spray dynamics by describing the formation phase, stable phase and dissipation phase
- Simulation and documentation of the trigger process by force-path diagram or velocity profile of actuator mechanism
- Free expansion of spray cone within the measuring zone
- Adaptation to different types of nasal sprays
- Measurement from finest droplets up to coarse drops
Download application notes for detailed information
Are you interested in additional content? Please register an account. After confirming the registration link brochures, application notes and other documents on particle measurement will be available for download.
Application strengths
- SPRAYER adapter for integration and trigger of different types of nasal sprays
- Q(t) trend diagram for time-resolved measurement of spray shot and identification of different spray phases
- Reproducible measurement of a spray shot’s stable phase
- Open measuring zone for measurement of freely expanded spray cone
- Recording of force-path diagram and velocity profiles during trigger process
- Measurement at defined inclination (0° to 90°) when using ROTOR
Customer benefits
- Development of sprays which guarantee a good deposition of drugs on mucous membrane
- Application-oriented droplet size analysis of finely to coarsely dispersed aerosols
- Targeted optimization of dosing pump systems and squeeze bottles for spray preparation
- Characterization of finger forces for the release of a spray dosage with therapeutically favorable droplet size distribution
- Flexibly adaptable measuring systems for different spray applicators
- Fast measurements with minimal preparation and cleaning effort
- Modular measuring system expandable for changing applications within the pharmaceutical development (powders, granules, suspensions, emulsions …)