Particle size and particle shape of graphite powder
Graphite is a natural manifestation of pure carbon with a special hexagonal crystal structure that is arranged in several parallel levels, called graphene layers. This anisotropic structure gives the graphite special properties, such as electrical conductivity or a particular strength along the individual layers, as well as slight fissility and good sliding and lubricating properties. On top of that, it is extremely heat-resistant with a sublimation point of over 3,800°C, thermally highly conductive and chemically inert. Its use as a material is accordingly diverse, e.g. for electrodes, batteries or sliding contacts (brushes), in refractory products and melting pots, for composite materials, self-lubricating bearings or generally as a dry lubricant. Naturally occurring graphite is mined and processed. However, graphite is also artificially manufactured in significant quantities by coking suitable carbonaceous materials and subsequent pyrolysis (graphitisation) in the required qualities.
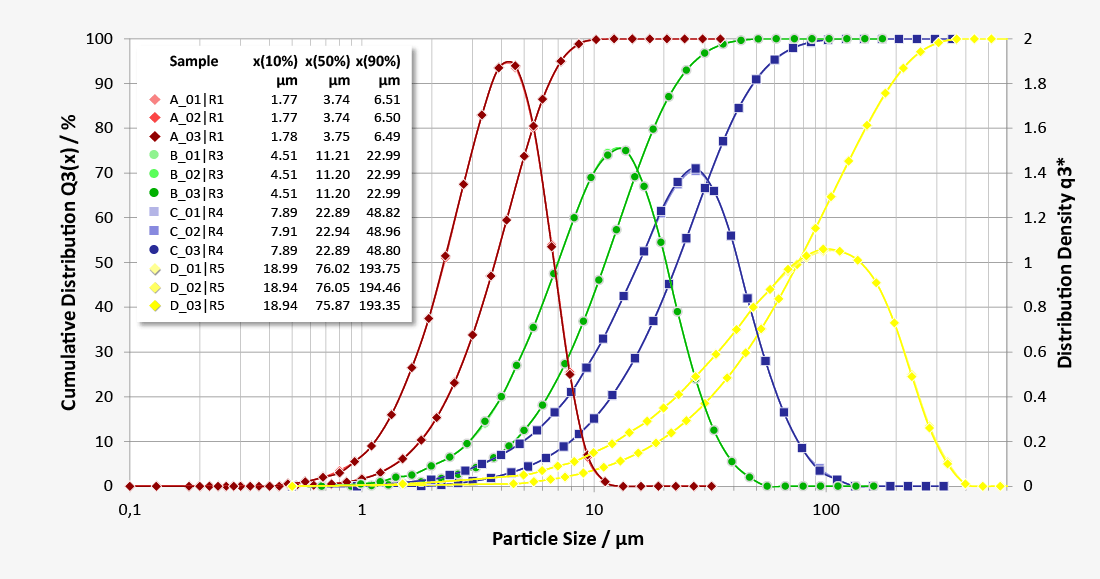
The final particle size of the graphite required for further processing or direct application is achieved using various grinding processes The size, shape and size distribution of the particles is ultimately determined by the functional properties of the graphite and the quality of the final products. Traditional screening analysis and microscopy are often still used to analyse the particle size and particle shape. The laser diffraction and dynamic image analysis provide significantly more powerful methods of characterising the size and shape of the graphite particles.
- Measurement over the entire particle size range with very good resolution
- Easy sample preparation
- Automatic setting of all measuring parameters
- Short measuring times for high sample throughput
- High reproducibility and good comparability of the measurement results
Download application note for detailed information
Are you interested in additional content? Please register an account. After confirming the registration link brochures, application notes and other documents on particle measurement will be available for download.
Dry measuring graphite powders using the HELOS/BR laser diffraction system with RODOS dry dispersion reliably delivers highly accurate and repeatable measurement results as high-resolution particle size distributions with 31 size classes. Small sample sizes of typically less than one gram can be measured in less than 30 seconds.
Application strengths
- Fast and reliable dry dispersion with RODOS | No dispersants required
- Identical measurement conditions for fine and coarse material
- Dry dispersion unbeatably fast | 3 measurements of a batch within 1 to 2 minutes
- Less cleaning overhead
- Very good repeatability
Customer benefits
- Fast and reliable process control to avoid faulty batches
- Optimum management of the grinding process
- Reliable quality monitoring
- Good comparability between systems means that specifications can also be maintained at remote production sites
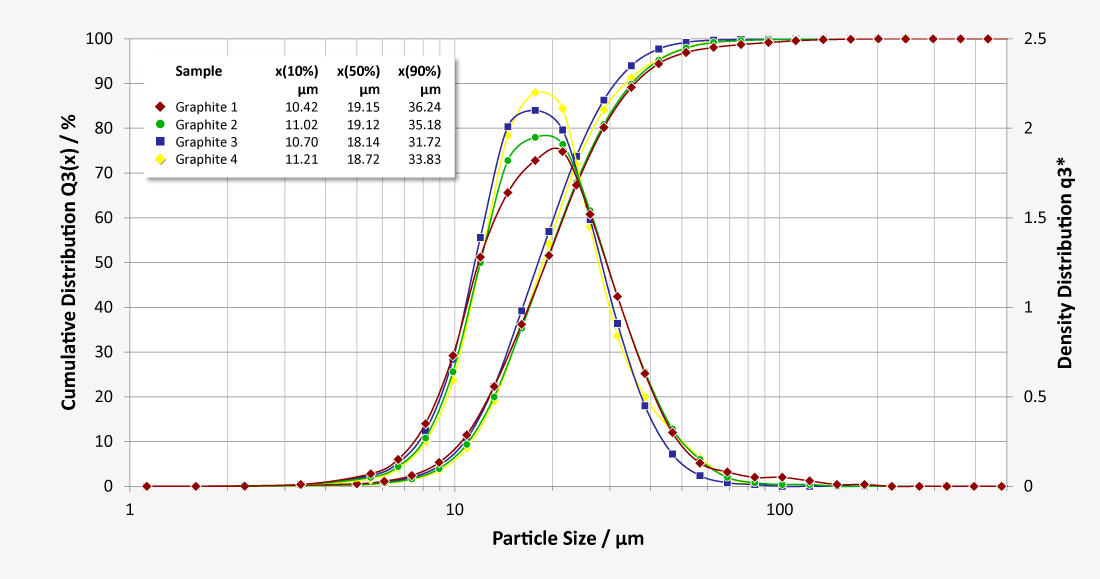
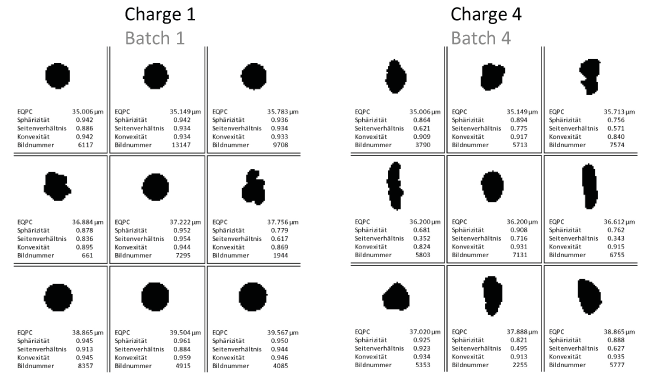
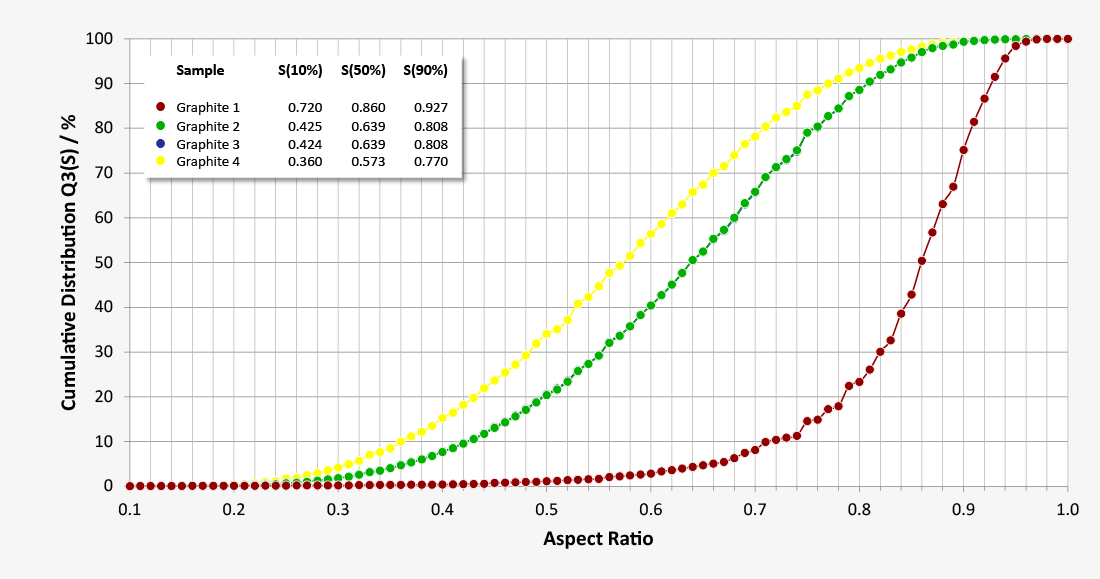
Batches with similar particle size distributions sometimes have significantly different properties in further processing and different qualities of the end products. Here it is worth using the dynamic image analysis with QICPIC to gain a complex insight into the particle shapes and different shape parameters.
If, for example, you consider the aspect ratio as a shape parameter – i.e. the maximum dimension of a particle in relation to the minimum dimension – there are significant differences between the four batches. For example, Batch 4 (S50%, 4=0.57) has a significantly higher proportion of long particles on average compared to Batch 1 (S50%, 1= 0.86).
Application strengths
- Characterisation of product properties by shape factors such as sphericity, convexity and aspect ratio
- Efficient dispersion of the graphite samples thanks to powerful wet disperser
- Best shape identification for finest samples
Customer benefits
- Stable product quality
- Improved incoming goods inspection
- Fewer batches outside of the specifications